Each year, over 82 million people worldwide contract gonorrhea, an STI that is spreading faster than most realize. As if that’s not enough, in cities across Europe and the U.S., the rising case numbers are now paired with a more serious threat: drug-resistant strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae that outpace conventional treatments.

This growing public health challenge highlights the need for urgent individual awareness. People need to approach sexual health with the same vigilance they would any other preventable medical condition.
In this guide, we break down what you need to know to spot gonorrhea early, understand how it spreads, and select the most suitable testing approach. Read on to protect your health and make confident decisions based on medical facts, not guesswork.
What is gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It primarily targets the mucous membranes of the genitals, but can also infect the rectum, throat, and eyes, typically through oral or anal sex. While it’s often associated with genital symptoms, extragenital infections are becoming increasingly common and frequently go undetected.
The infection is most prevalent among sexually active individuals aged 15 to 24, particularly those with multiple partners or inconsistent condom use.
How is gonorrhea transmitted?
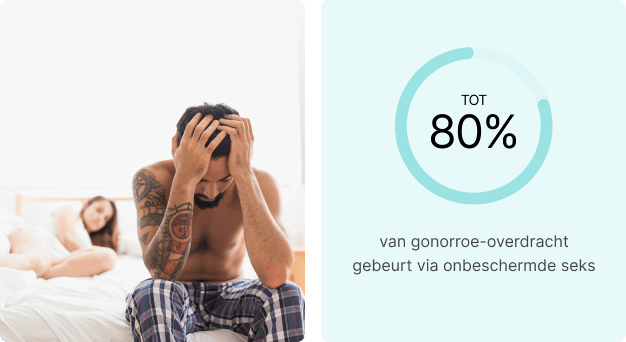
Gonorrhea is transmitted through unprotected vaginal, anal, or oral sex with an infected partner. The bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae thrives in warm, moist areas of the body, particularly the urethra, cervix, rectum, and throat. Because of this, it spreads easily through mucous membrane contact, even in the absence of ejaculation. Direct exposure to infected secretions is enough to transmit the infection.
Perinatal transmission is also possible. If left undetected during pregnancy, gonorrhea can pass from mother to child during delivery, causing severe eye infections that may result in permanent vision damage.
Key risk factors include:
- Having unprotected vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
- Multiple or new sexual partners.
- A history of sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- A partner diagnosed with an STI.
- Belonging to sexual networks with high STI prevalence (e.g., MSM communities).
Public Health Insight: In the Netherlands, gonorrhea has remained a consistent concern for decades; it was already among the top four most reported STIs back in 2005.
What are the early symptoms of gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea can cause symptoms as early as 2 days to 3 weeks after exposure, but in many cases, it remains silent, especially in women. This makes early detection challenging and increases the risk of unknowingly transmitting the infection to others.
When symptoms do occur, they typically vary depending on the site of infection. Here’s what gonorrhea feels like:
Genital symptoms:
- Burning or pain during urination
- Unusual discharge from the penis or vagina (white, yellow, or green)
- Vaginal bleeding between periods
- Swollen or tender testicles in men
Rectal symptoms:
- Anal itching or discomfort
- Rectal discharge
- Bleeding after bowel movements
Throat symptoms (oral gonorrhea):
- Persistent sore throat without cold or flu symptoms.
These early signs can overlap with other STIs like chlamydia, so testing is the only way to confirm a diagnosis.
Can you have gonorrhea without symptoms?
One of the most concerning aspects of gonorrhea is how often it goes unnoticed. According to the Cleveland Clinic, up to 50% of women and 10% of men with genital gonorrhea experience no symptoms at all. Infections in the throat or rectum are even more elusive; about 90% of people with oral or anal gonorrhea report no symptoms.
Even with genital infections, symptoms are not guaranteed. While 90% of men typically notice signs, only 30% to 60% of women do. Without clear symptoms, gonorrhea can silently progress and cause serious complications like pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), epididymitis, or infertility.
This is why routine STI testing is essential, especially if you have multiple partners or engage in oral or anal sex. It’s the only way to catch the infection early and prevent long-term health risks.

Public Health Insight: Each year, around 20,000 people in the Netherlands are diagnosed with gonorrhea, and that only includes individuals who underwent STI testing. The actual number is likely higher due to undiagnosed, asymptomatic cases.
What are the symptoms in men and women?
Gonorrhea symptoms can vary significantly between men and women, and in some cases, they can be so mild that they go unnoticed. Understanding the differences is key to catching the infection early and preventing long-term health issues.
Common gonorrhea symptoms in men include:
- A burning or painful sensation when urinating
- White, yellow, or green penile discharge
- Pain or swelling in one testicle (less common but concerning)
- Rectal pain, discharge, or bleeding in cases of anal infection

Gonorrhea symptoms in women may include:
- Painful urination or a frequent urge to go
- Increased vaginal discharge, often with an unusual odor or color
- Bleeding between periods
- Lower abdominal or pelvic discomfort
- Rectal irritation or discharge, which occurs when the infection spreads beyond the genitals

What are the risks of untreated gonorrhea?
Without treatment, gonorrhea progresses. The infection can cause serious, sometimes irreversible health problems, depending on the site of infection and the person affected.
In Women, untreated gonorrhea may lead to:
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): A severe infection of the uterus and fallopian tubes that can cause chronic pain, scarring, and infertility.
- Ectopic pregnancy: Scarring from PID increases the risk of pregnancy occurring outside the uterus, which can be life-threatening.
- Chronic pelvic pain: Inflammation can leave long-term damage even after the infection is gone.
In Men, risks include:
- Epididymitis: Painful inflammation of the tube that stores and carries sperm, potentially affecting fertility.
- Prostatitis: Infection of the prostate gland, which may cause pain, fever, and urinary issues.
- Reduced fertility: Ongoing inflammation can impact sperm health and flow.
In both sexes:
- Disseminated Gonococcal Infection (DGI): The bacteria can spread to the bloodstream, causing symptoms such as joint pain, skin lesions, or even sepsis.
- Gonococcal arthritis: A painful swelling in one or more joints due to the bacteria spreading beyond the initial infection site.
- Increased HIV risk: Gonorrhea increases both the risk of acquiring and transmitting HIV by compromising mucosal barriers and increasing local inflammation.

In newborns, Infants exposed to gonorrhea during vaginal delivery can develop a severe eye infection known as ophthalmia neonatorum. If left untreated, it can lead to permanent vision damage or blindness. Research shows that up to 28% of babies born to mothers with gonorrhea may develop this condition.
Additionally, they’re also at risk for joint infections or life-threatening sepsis. Early detection during pregnancy is critical.
How can you detect gonorrhea early?
Early detection is key to preventing gonorrhea complications, mainly because the infection often causes no symptoms at all. The most reliable way to identify gonorrhea is through routine STI screening.
Testing is essential for:
- Sexually active women under 25
- Men who have sex with men (MSM)
- Anyone with new or multiple partners
- Individuals with symptoms or a partner diagnosed with an STI
- Pregnant individuals to prevent complications during delivery
For individuals in higher-risk groups, get tested every 6 to 12 months, or more frequently, as recommended by your doctor. Platforms like Easly make early detection easier with accurate at-home gonorrhea testing kits. These are especially useful if you prefer privacy, live in remote areas, or want to avoid clinic wait times.



What are the westing options for gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea can be diagnosed using several testing methods, each suited to different needs and situations:
- Nucleic Acid Amplification Test (NAAT): This is the gold standard for diagnosing gonorrhea. It detects the genetic material of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in urine or swab samples (vaginal, rectal, throat, or urethral). NAATs are highly sensitive and specific and are performed in a certified laboratory.
- At-home sample collection kits: These offer a discreet, clinically reliable way to test without visiting a clinic. You collect a sample, usually urine or a swab, at home and mail it to a certified lab for analysis. Platforms like Easly offer STD Basic and STD Complete tests that screen for gonorrhea and other common STIs. Results are typically returned within a few days via a secure online portal.
- Rapid tests: A few point-of-care rapid gonorrhea tests provide results in under 30 minutes. While promising for clinical settings, these are less accurate than NAATs and not widely available for home use.

Each option varies in availability, accuracy, and privacy. For most people, either a lab-based NAAT or a certified home test from providers like Easly offers the best balance of clinical quality and convenience. Easly offers STD basic and STD complete home tests that screen for gonorrhea and many other common infections, adding to your convenience.
How does at-home gonorrhea testing work?
At-home testing allows you to screen for gonorrhea privately and accurately. Here’s how it typically works:
- Order a test kit from a certified provider like Easly.
- Collect your sample, usually a urine sample or swab, by following detailed instructions.
- Return the sample using the prepaid envelope included in the kit.
- Receive your results online within 2 to 5 business days.

These kits are processed in accredited laboratories using the same NAAT methods used in clinics, ensuring medical-grade accuracy. They are particularly valuable for individuals who prefer privacy, live in remote areas, or want to test without the wait times or stigma associated with clinics.
When should you choose lab testing?
While at-home testing is a safe and reliable option for many, there are situations where clinic-based testing is the better choice. These include when:
- Symptoms are present, such as discharge, pain during urination, or pelvic discomfort.
- Exposed to the STI after unprotected sex with a diagnosed partner.
- Pregnant or planning for conception to protect both maternal and infant health.
- Urgent results are needed (some clinics provide same-day testing and treatment).
- A physical exam or immediate care is required, especially for complications.

Clinics also facilitate comprehensive STI screening, counseling, and partner notification support, key components of effective public health management.
How accurate are at-home vs. lab tests?
Certified at-home gonorrhea tests using NAAT technology offer 95–99% accuracy, comparable to clinic-based testing, when used correctly and administered by a healthcare professional. The key difference lies in sample collection:
- In clinics, trained professionals collect samples, reducing the risk of error.
- At home, accurate results depend on following instructions closely.
For added assurance, some individuals choose to follow up with a lab test after a positive at-home result.
When should you see a doctor?
Consult a doctor if:
- You develop symptoms such as discharge, painful urination, or pelvic pain.
- You or your partner tests positive for gonorrhea.
- Symptoms don’t resolve after completing treatment.
Prompt medical care reduces complications and limits further transmission.
How is gonorrhea treated?
The recommended treatment for uncomplicated gonorrhea is a single intramuscular injection of ceftriaxone (500 mg), administered by a healthcare professional. This medication should not be self-administered without medical supervision. If chlamydia is also present, oral doxycycline may be added. Always complete the full course of treatment and avoid sexual contact for 7 days after treatment or until all symptoms have resolved.

Can you get reinfected after treatment?
Gonorrhea treatment clears the current infection but does not provide immunity against future infections. Without follow-up care or treatment from a partner, reinfection remains a significant risk. To reduce the chance of reinfection:
- Get retested after 3 months, even if you’re symptom-free
- Ensure all recent partners are tested and treated
- Use condoms consistently
- Test regularly if you have new or multiple partners
Conclusion
Gonorrhea is not a mild inconvenience; it’s a fast-moving bacterial infection that can silently damage reproductive health, increase the risk of HIV, and threaten infant health during childbirth. It demands action, not delay.
Recognizing symptoms is essential. However, relying solely on symptoms is not enough. The infection often spreads without any warning signs, especially in the throat, rectum, or cervix.
If you’re sexually active, particularly with new or multiple partners, routine testing is a medical necessity. It’s the only way to catch gonorrhea early, treat it effectively, and avoid long-term complications.
Easly’s STD Basic, STD Complete, and STD Budget home tests offer certified, lab-grade accuracy with complete privacy. They’re trusted, fast, and designed to help you act before it’s too late.
Take control of your sexual health, test early, test smart.
Sources
- World Health Organization. Gonorrhoea
- CDC. Drug-Resistant Gonorrhea
- CDC. About Gonorrhea
- Healthline. Everything You Need to Know About Gonorrhea
- MedLine+. Gonorrhea (Also called: The clap)
- Soaaids. Gonorroe.
- RIVM. Gonorroe
- Thuisards. Ik heb gonorroe
- Cleveland Clinic. Gonorrhea